Guide to Google Ads Display Ads
Now that you’ve ‘graduated’ from our Everything You Need to Know About AdWords Guide, we’re going to dive deeper into one of Google’s two advertising network options: Display Ads. Google Display Network (GDN) has some super targeting and formatting options for eCommercers, and if optimized correctly for the right product and store, it can bring some juicy traffic.
The first thing to understand about Display campaigns is how they differ from search. The main difference is the behavior or state of mind of the person who is seeing a search or Display ad. With search ads, your audience is in ‘look mode’; they are actively searching for what you are offering. With Display ads, however, you are reaching potential customers while they are busy doing something else. This means that Display ads require a different approach than search. That’s not to say they aren’t effective or have their advantages.
One of the biggest reasons GDN is popular among PPC advertisers is its targeting options. Google Display allows you to target your potential customers by topics, keywords, retargeting and placement, providing a wider variety of options than search. (We will get into this in more detail further in the post.)
The first consideration, before you think of how to run a Display ad, is to ask yourself whether you should be running Display ads at all. Why? Because the truth is, Display ads do not work for every niche or online store. Here are some questions you should be asking yourself when planning out your GDN strategies.
- Do you have the creative budget or know-how to create visually appealing ads?
- Do you have specific deals or products you wish to push, or are you looking for brand awareness?
- Do you want to pay less per click? (Display ads generally cost less per click than search ads.)
- Do you want to drive traffic to your product pages without having to compete with big competitors (or your suppliers) on search?
- Do you want better quality scores, as you have options to target specific topics and interests?
If you answered yes, then Display ads could be an effective addition to your traffic-driving strategy. This beginners’ guide to Google Ads Display ads answers all your questions and more, so let’s jump right in!
Google Display Types, Sizes and Formats
Google Display Types
There are four types of Google Display Ads to choose from: Video, Image, Text & Rich Media
Video Display Ads
Video Display Ads are ads that display with YouTube videos. There are three main types of video Display ads to choose from:
- Search display, which are displayed when a user searches for a specific keyword
- Stream display, which are those ads that show before or after a user watches a YouTube video
- In-Display: ads that appear next to the video while you’re watching
Video Google Display Ads are a good choice for those online stores that know their audience is watching video, have high video click-through rates and have the budget and the time to put together top notch video ads. Unlike social media videos, Display video metrics will be unforgiving of low-quality videos.
Image Display Ads
These are static image ads that display in blocks on websites in various sizes.
Text Display Ads
The same as Google Display Ads; these are text-only ads.
Rich Media Display Ads
These are interactive Display ads that change dynamically depending on who is seeing the ad and their engagement.
These ads require a little but more design and tech know-how and are therefore better suited for bigger businesses with bigger budgets for outsourcing design work.
Google Display Sizes and Formats
Display Ad Sizes
Google Display Ads offer advertisers over 20 different block sizes and dimensions. Here are the top-performing ad sizes according to Google.
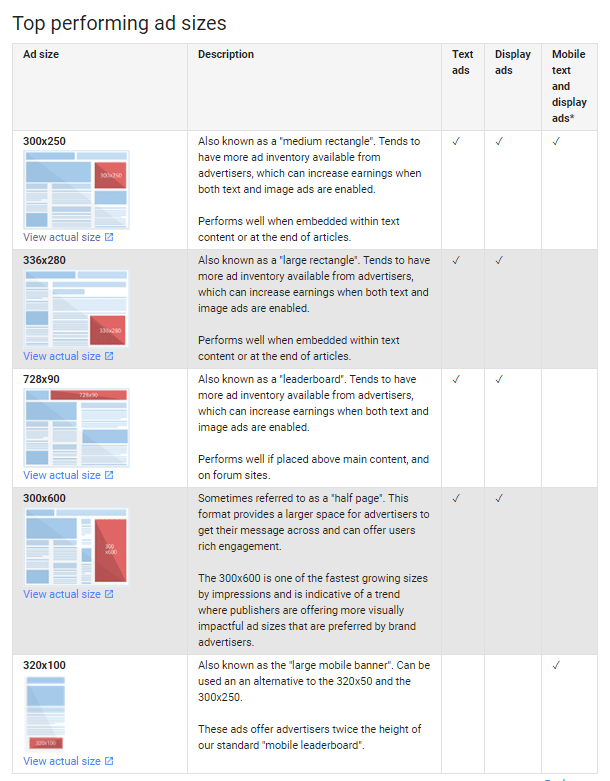
There are a variety of sizes to fit your store advertising budget and preference. Here’s a complete guide from Google: guide to ad sizes.
Display Ad Technical Requirements
- All ads needs to be 150KB or smaller
- Interactive/animated ads should be a maximum of 15 seconds
- GIF slide ad speeds should be 5 frames p/s
- Flash ads should exceed the speed of 20 frames p/s
Google Display Targeting Options
As we mentioned at the start of the AdWords Guide, there are four main targeting options: Keyword, Placement, Topic, and Interest targeting. Here’s a breakdown of each.
Display Keyword Targeting
Implemented only a year ago, GDN keyword contextual targeting is the most widely used targeting option. When using this targeting, your ads would be shown based on your potential shopper’s recent search history and other factors, not by the content relevance of the page they are viewing when seeing your ad. To set up this kind of targeting, follow these steps.
Step 1: Set Up Your Keyword list
First, like you would with your search campaigns, you will need to research the keyword words and terms you would like to use for your Display ads.
Step 2: Choose Keyword Targeting
Once you have found the right keywords, you will then set up your campaign according to this targeting. like this
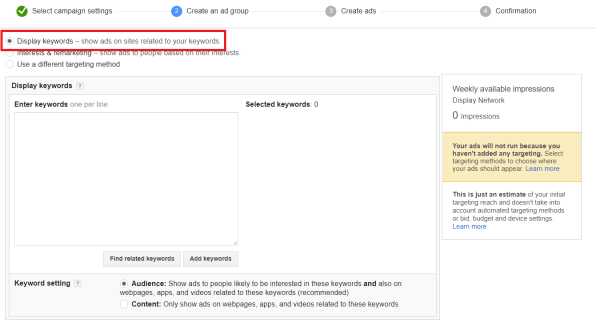
Pro Tip: For GDN, keep your keyword list small, around 5-20 very related keywords and phrases that are highly relevant to your ad content.
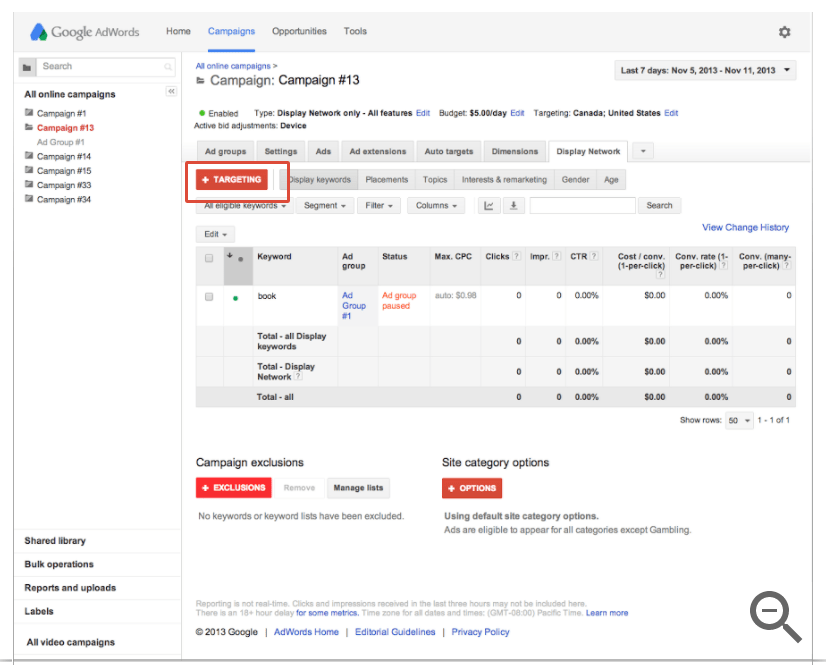
Step 3: Optimize
You will want to check which websites are displaying your ads and clicks and optimize accordingly. You can do that here:
Display Placement Targeting
As the name suggests, these ads target specific websites, therefore giving you maximum control over where your Display ads will be displayed. Using this targeting is for those eCommerce advertisers who want to match their ads to very specific content within their niche and/or those sites you know your potential shoppers are hanging out at (reading).
If you’re looking for ideas, give AdWords’ Display Planner a try.
Display Topic Targeting
Display topic targeting allows you to target your ad placement based on topics. You can find this by selecting ‘Use a different targeting method’ and then selecting topics.
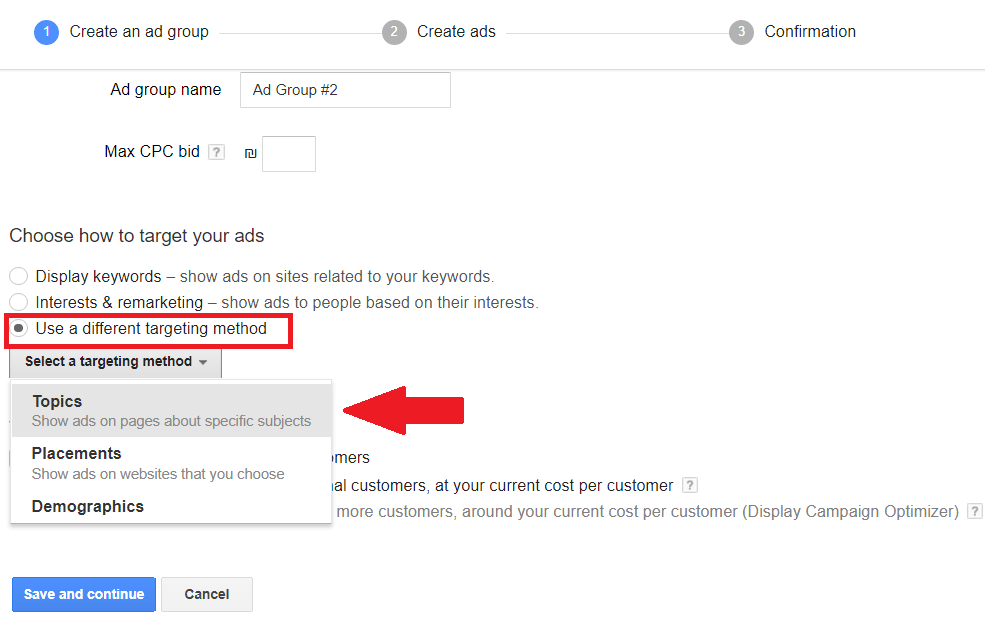
Here you have a variety of niche-related topics to choose from. For example, if you’re selling kitchen gear, you could look for topics such as food and drink > cooking or hobbies and leisure to make sure your ads are displayed on food/cooking-related blogs that:
- Make your ads more relevant
- Are shown to people in your desired audience
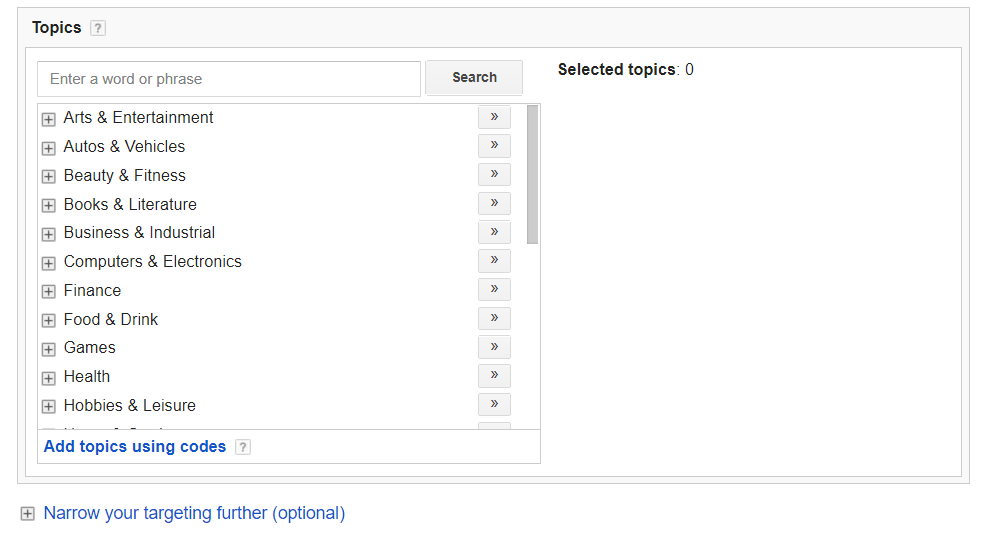
The drawback to this type of targeting is that, unlike facebook custom audiences, topic targeting can be on the broad side.
Display Interest Targeting
With a similar ‘topic’ list to selecting topic-based targeting shown above, interest allows you to target based on a user’s interest instead of the content of the page. Meaning, Google will show ads to users regardless of what page they are on if their interests match up with your interest targeting. This works with cookies that Google uses to store the information and behavior of browser users, to be able to know what kinds of things they are regularly interested in.
Display Remarketing
The final type of display targeting options are remarketing.
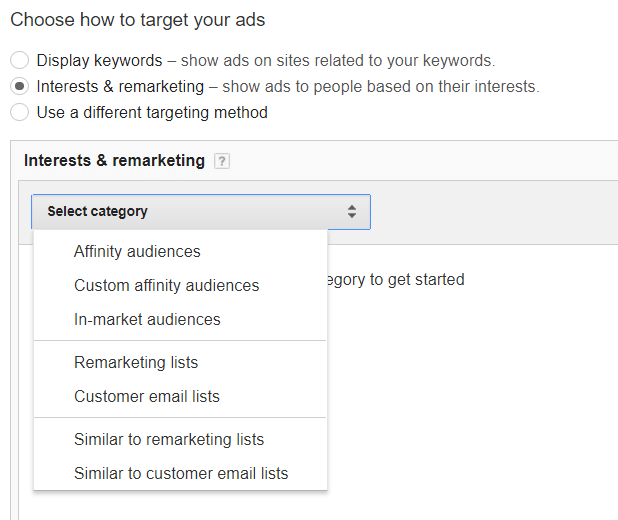
This targeting allows you to display ads to those online people who have already bought from you, visited your site or engaged with your brand, regardless of which site they are on. You are able to set up a variety of remarketing lists that enable you to target engagement differently from people who have just visited to your homepage or those who have viewed a specific video.
How to Set Up Your First Display Campaign
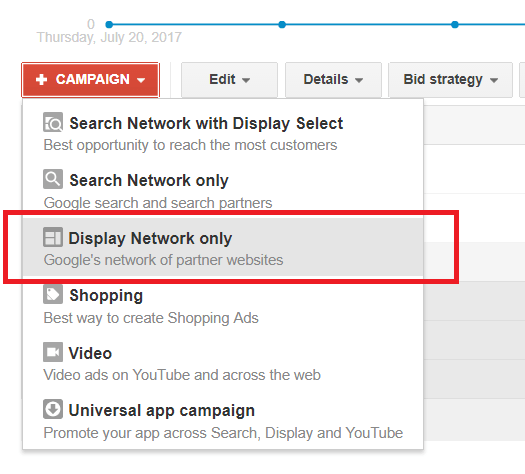
Step 1: New Campaign > Display Network
Step 2: Marketing Objectives
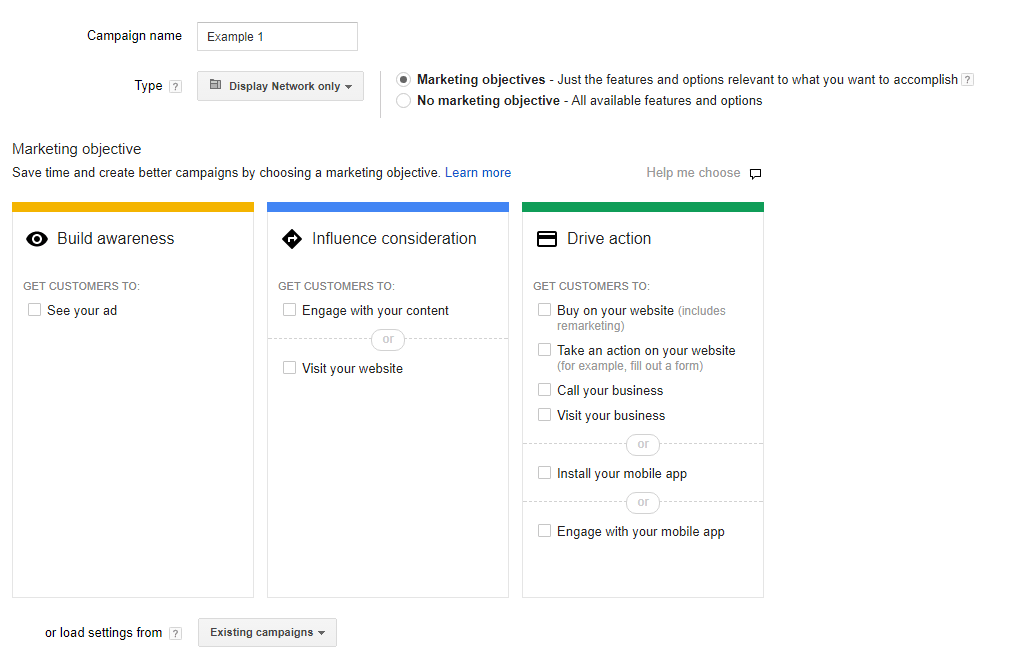
For Display newbies, Google gives you the option to identify your objective. it then provides sub-options around that intention throughout your campaign setup to prompt decisions that will live up to the strategy.
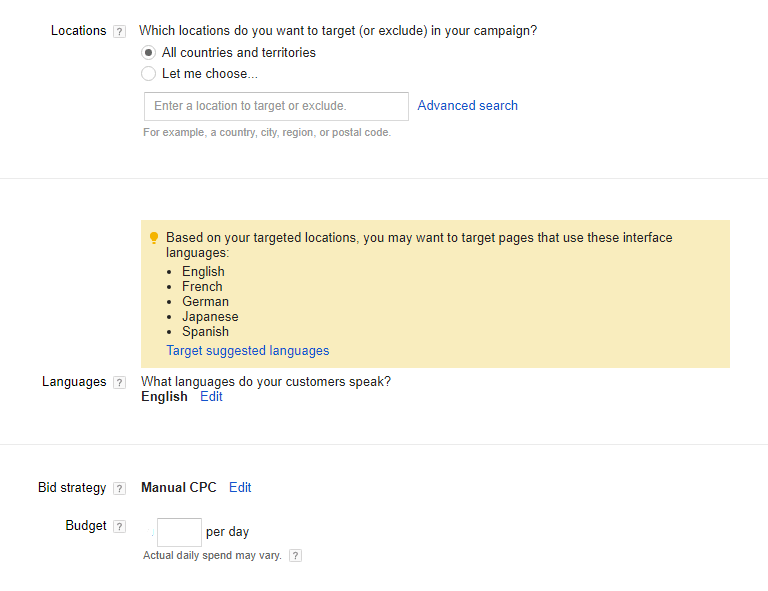
Step 3: Choose Location, Language and Budget
Step 4: Select Additional Settings
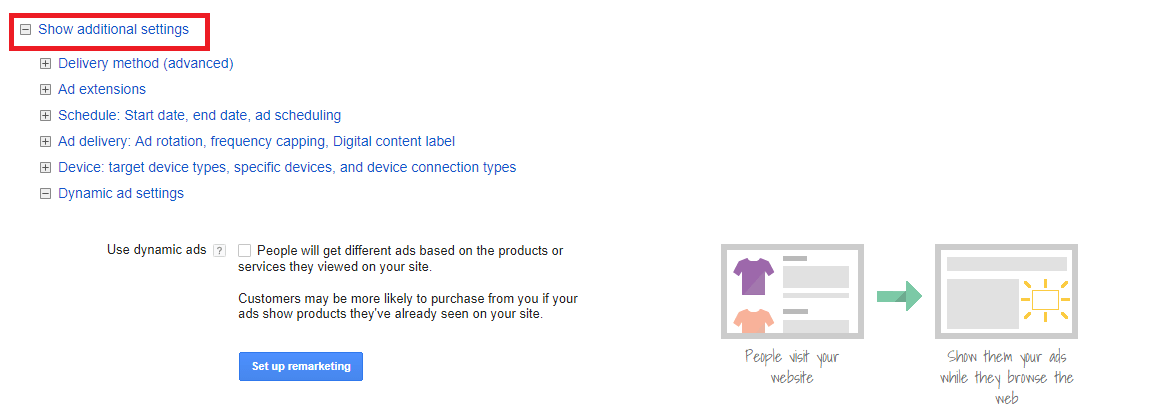
This is where you can adjust things like campaign schedule times, set whether you want accelerated delivery or set up dynamic ads.
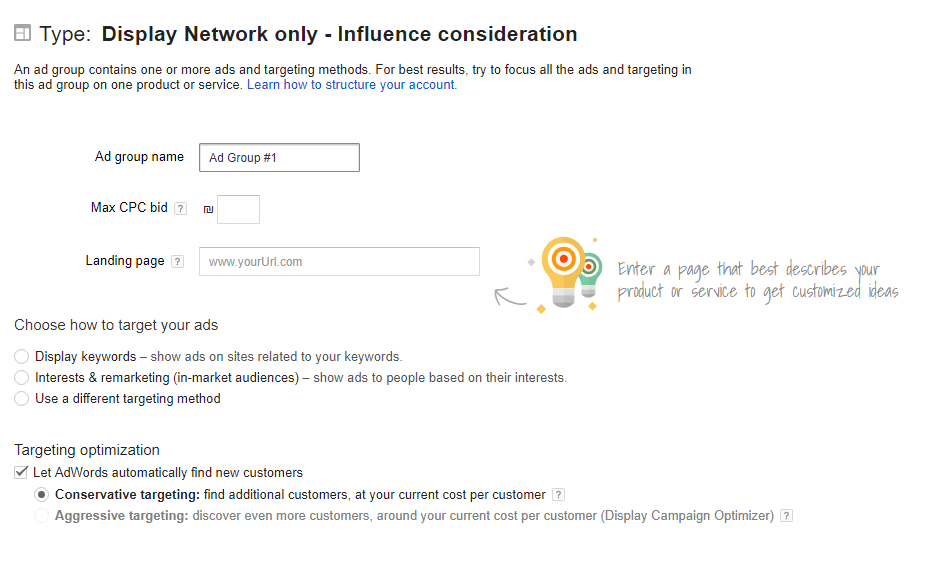
Sep 5: Adgroup Set Up and Targeting
Next, you will need to name your Ad Group and input your targeting options, which we outlined above.
Pro Tip:
If you’re new to Display ads but already have a good stream of steady traffic you’re generating from AdWords search, Facebook ads or other PPC means, start with retargeting. Starting with retargeting will give you the best gauge on how you can expect to perform on this PPC platform. Mark Irvine, PPC strategist, stated, “If you’re ever going to see any kind of return on the display network, you’re going to see it from remarketing first.” Remarketing allows you to target people who already know you, making it far more likely that you will get those ad clicks.
Step 6: Create Your Display Ad
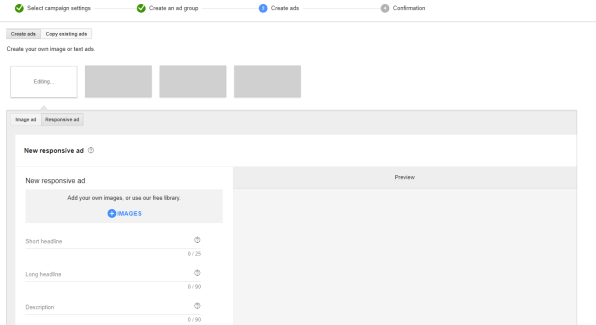
The final step is to create your ad. Here you can build an image or responsive ad type, or upload your Display ad HTML5 A file. Here are some additional Google Display ad tips to get you started.
- Keep your ads relevant to your desired target audience, and the landing page content they will see when they click through
- Have a clear call to action
- Use good-quality images
- Focus on and create ads designed for your ideal customers
- When it comes to Display ads, design matters!
Bonus: Google’s Smart Display Campaign Options
Display’s newest addition is Google’s smart display campaigns that automate ad layouts, bidding and targeting. Put simply, these ads will adapt responsively and dynamically, using a variety of types and sizes depending on who is seeing the ad and which products they have seen in your store.
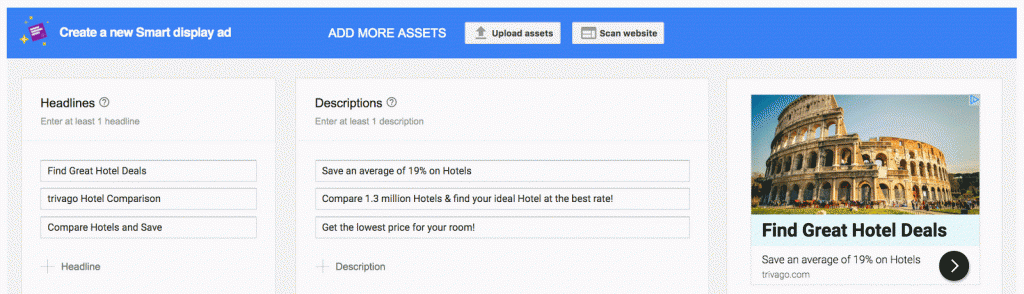
According to Google: “Smart display campaigns offer a simple, intelligent solution to managing the complex variables of display advertising, and may be the most effortless way to broaden your customer base and win new conversions. Use a Smart display campaign to show ads in almost all formats across the Google Display Network, reaching people at all stages in the buying cycle—from people with demonstrated interests to customers just about to buy.”
This is a great alternative for those smaller online stores who don’t have the budget or the time to get professional design work done.
Final Thoughts: Display Campaign Optimization
Finally, like with all PPC campaigns, you will need to regularly monitor and optimize your Display ads. To this you will want to exclude irrelevant categories and audiences, review where your ads are being displayed, checking ad performance geographically and site locationally.
If you have any AdWords questions, drop us a comment below and our PPC gurus will get in touch.